Seeing is Believing: Octant Reveals the Objects Running in Kubernetes Clusters
In a perfect world, you would deploy applications to clusters and nothing else would be a problem. In the Kubernetes world, it isn’t that simple yet. Because Kubernetes workloads are composed of multiple objects, even simple actions can be complex. This complexity is why we created and open sourced Octant, a developer-centric web interface for Kubernetes that lets you inspect a Kubernetes cluster on which applications reside. Check out Octant on GitHub.
To help a developer better understand the state of the application running inside the cluster, Octant’s dashboard allows you to navigate through your namespaces and the objects they contain. It lets you visualize the relativity of objects and resources. Unlike the Kubernetes Dashboard, Octant runs locally on your workstation and uses your Kubernetes credentials to access the cluster, an approach that avoids a whole class of security concerns.
There are myriad dashboard projects for Kubernetes. What new features does Octant bring to the table?
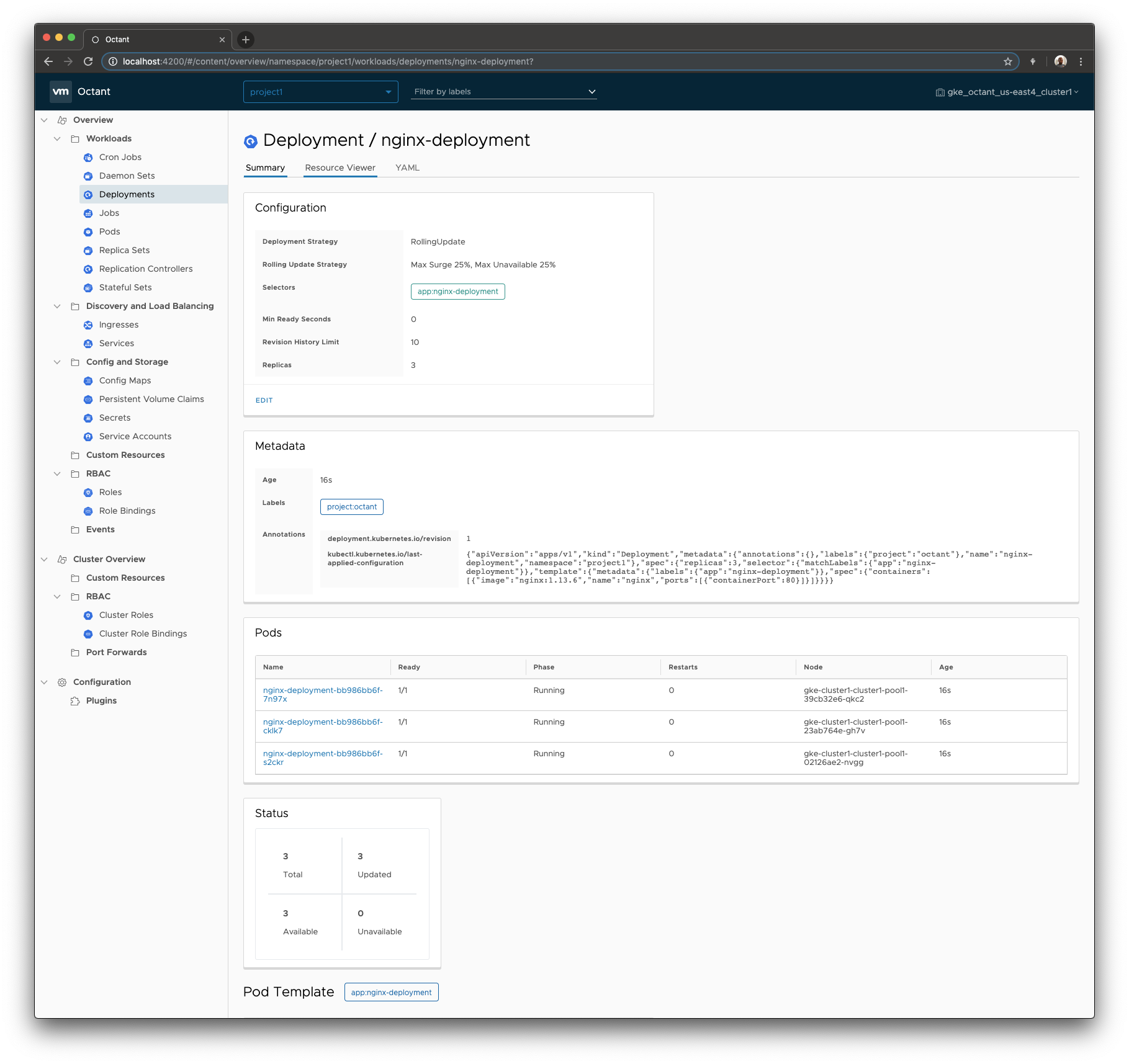
Visualizing workloads
Octant was created to help you inspect your workloads. Determining whether a workload is up on Kubernetes and running as designed is complex because an application can be a Deployment coupled with a Service, an Ingress object, and many other objects. To give developers a complete view, Octant creates a real-time graph of related objects. A Deployment maintains at least one ReplicaSet, which maintains at least one pod. Octant can find and show these objects. Pods have a ServiceAccount and can be associated with one or more Service objects, which can belong to one or more Ingress objects. Octant can find and show these objects as well.
With a complete view of an object and all its related objects, you can more accurately assess the status of applications and avoid unfocused debugging when things go wrong
Octant is a tool built for extension
There isn’t one true way to manage a Kubernetes cluster. There are entire ecosystems of tools for creating and managing objects, providing observability, and working with continuous integration and delivery tools. With Octant, you can integrate those ecosystems into one convenient browser-based user interface. Octant provides a plugin system that allows you to add information to your cluster views. You can embed usage graphs to pods, add information to Ingresses, and highlight objects that have recently been updated through continuous delivery. Plugins let you integrate information about objects where it is most useful.
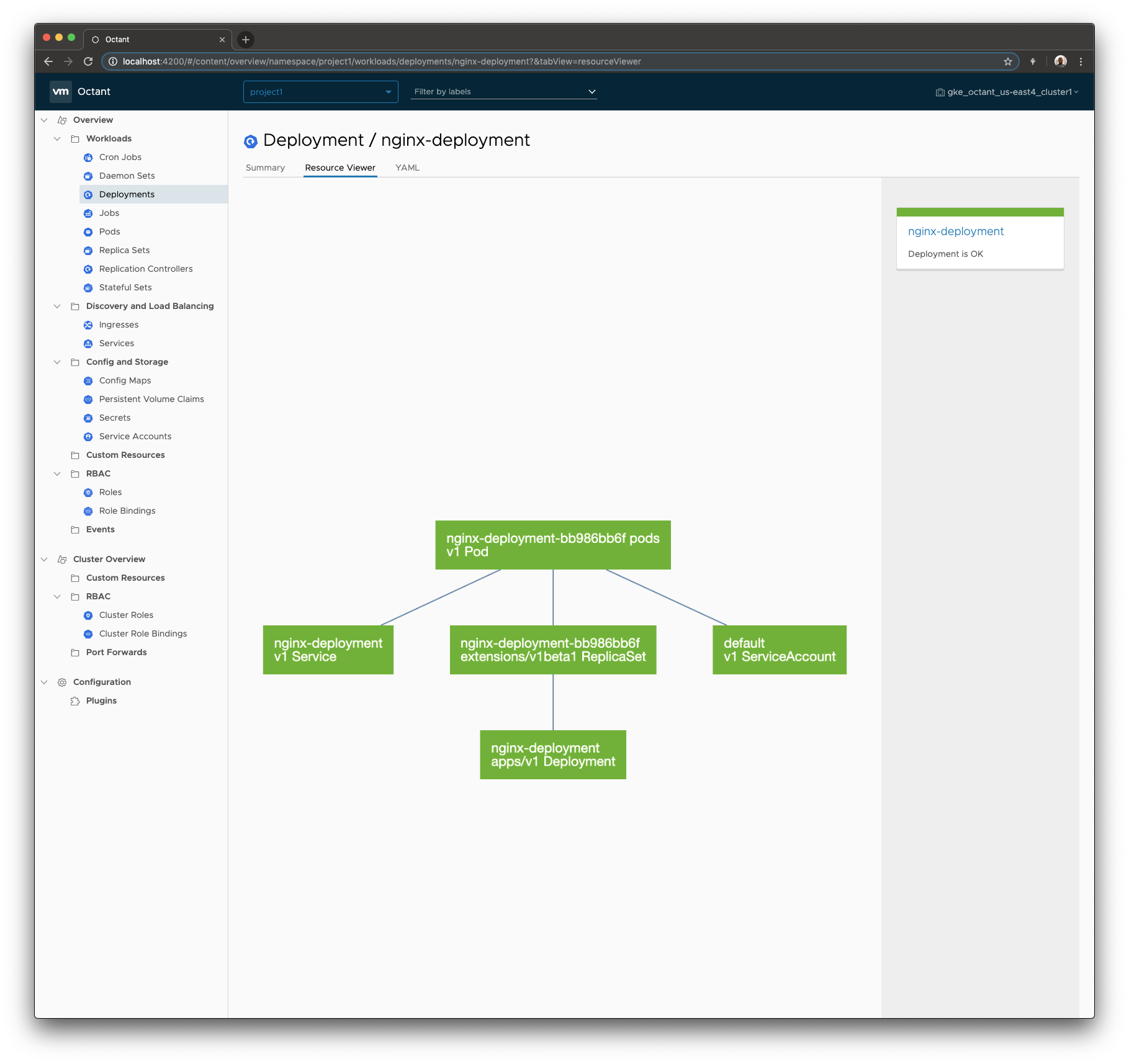
Octant
Octant isn’t simply a consumption tool. Plugins have real-time access to the cluster and will be able to manage objects even when they aren’t being viewed in the dashboard.
Support for custom resource definitions
One of the most powerful features of Kubernetes is the ability to extend its API using custom resource definitions. Octant can display custom resource definition objects in real-time and take advantage of custom columns. If our vision for Octant plays out according to our current plans, Octant will use the embedded schemas to determine whether custom resources are configured correctly. The ability to see custom resources would allow users of Octant to have a more complete view of what is running in a cluster.
With Octant’s plugin API, authors can create views for custom resources as rich as the built-in objects. Plugin authors can generate intuitive editors for managing custom resources in a visual way.
We are only at the beginning
We’ve opened Octant to the community for everyone to use and provide feedback on. Our hope is to make the process of managing workloads in a cluster easy and something anyone can do. The goals of the project are to:
Provide a visual interface to managing Kubernetes that complements and extends existing tools like kubectl and kustomize.
Make it easy for developers to understand how their workloads are performing in a cluster. Create an extensible tool that provides a common integration point for the multitude of tools Kubernetes developers use to get software to production.
Get involved
The nature of Octant as a project requires input from the community to find its place within the Kubernetes ecosystem. From code contributions and documentation to sharing your usage in the field, there are many ways to get involved. Feel free to ask questions via the distribution list, Slack, or try out the latest release on GitHub!
- Easy first issues tag
- Propose or request new features
- Try writing a plugin
- Share how your team plans to use Octant
Join the Octant community
- Get updates on Twitter ( @projectoctant)
- Chat with us on Slack (# octant on Kubernetes Slack)
- Join the Octant Community Meetings

 Twitter
Twitter Slack
Slack RSS
RSS GitHub
GitHub